Essential oil — a good weapon in the age of antibiotic prohibition
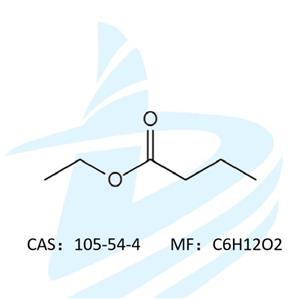
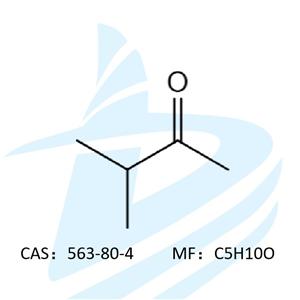
The chemical composition of essential oils is very complex, containing hydrocarbons, alcohols, ethers, phenols, acids, esters, aldehydes, ketones, lactones, etc. At present, there are more than 22,000 compounds that constitute essential oils, which can be summarized into four categories: terpenes derivatives, aromatic compounds, aliphatic compounds and nitrogen-containing sulfur compounds.
Terpenes are the main components of essential oils, including lavenderene, farnesene, and taxol, which are the most common types of plant extracts in nature; aromatic compounds are the second largest after terpenes Compounds, including terpene-derived derivatives (such as thymol, cumin phenol) and phenylmethane derivatives (such as cinnamaldehyde, star anise in star anise), this class is often used as antibacterial, production-promoting, spicy spices Aliphatic compounds are mainly small molecular compounds, which are relatively small in content, and almost exist in all essential oils, and there will be some non-essential oils; nitrogen-containing sulfur compounds contain nitrogen and sulfur, generally have a strong and spicy odor, Including our common allicin, onion trisulfide and so on.

Biological functions of essential oils
(1) The bactericidal and antibacterial functions of essential oils: Most essential oils of spices have anti-fungal, bacterial and other microbial activities, such as carvacrol, thymol, cinnamaldehyde and other essential oils, which have very strong antibacterial effects and are mostly safe and efficient Bacteriostatic, are used in food, aquaculture, feed and other fields. The synergistic effect of different essential oils can effectively improve the broad-spectrum antibacterial properties of essential oils and enhance the microbial inhibition and sterilization effect. The mechanism of action of essential oils on microbial sterilization and bacteriostasis can be summarized as its active components destroy cell membrane lipids and membrane proteins, affect the normal biological function of cell membranes, and cause bacterial growth to be inhibited or even killed.
(2) The function of essential oil to attract and promote growth: essential oil can be added as a flavoring agent in animal diets to increase the food intake, increase the feed intake, and improve the animal production performance. obvious. Essential oils can regulate the body's functions, enhance the animal's humoral immunity and cellular immunity, and help resist the attack of various germs and viruses. Essential oils can stimulate the development of intestinal villi, promote the secretion of various digestive enzymes in the intestine, improve the digestion and absorption of animals, and thus improve the digestibility of feed.
(3) Antioxidant function of essential oils: aldehydes, phenols and their derivatives in essential oil components have antioxidant functions. The antioxidant effect of essential oils is based on the ability to provide hydrogen or electrons for free radicals. The aromatic structure of some essential oils has the ability to modify unpaired electrons, which can protect their biologically active molecules from being oxidized.